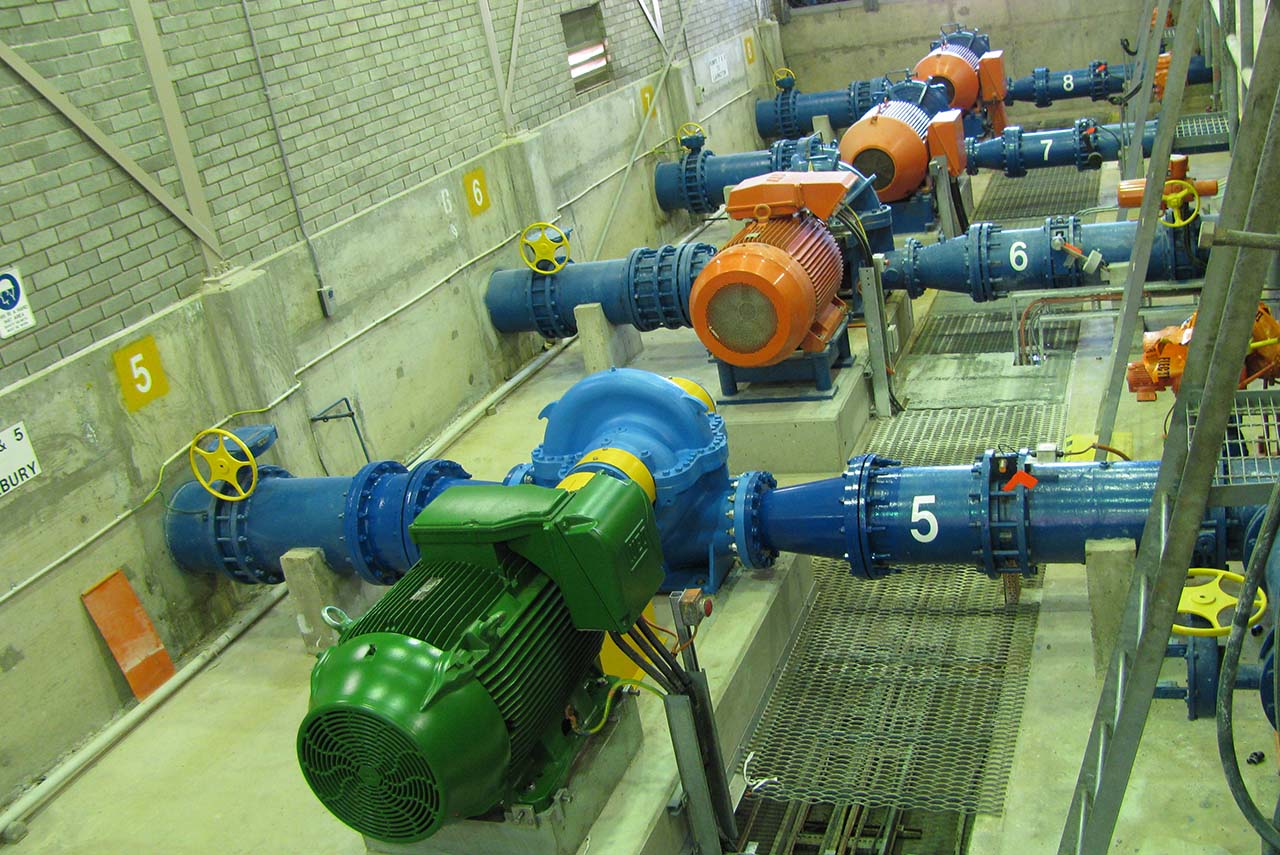
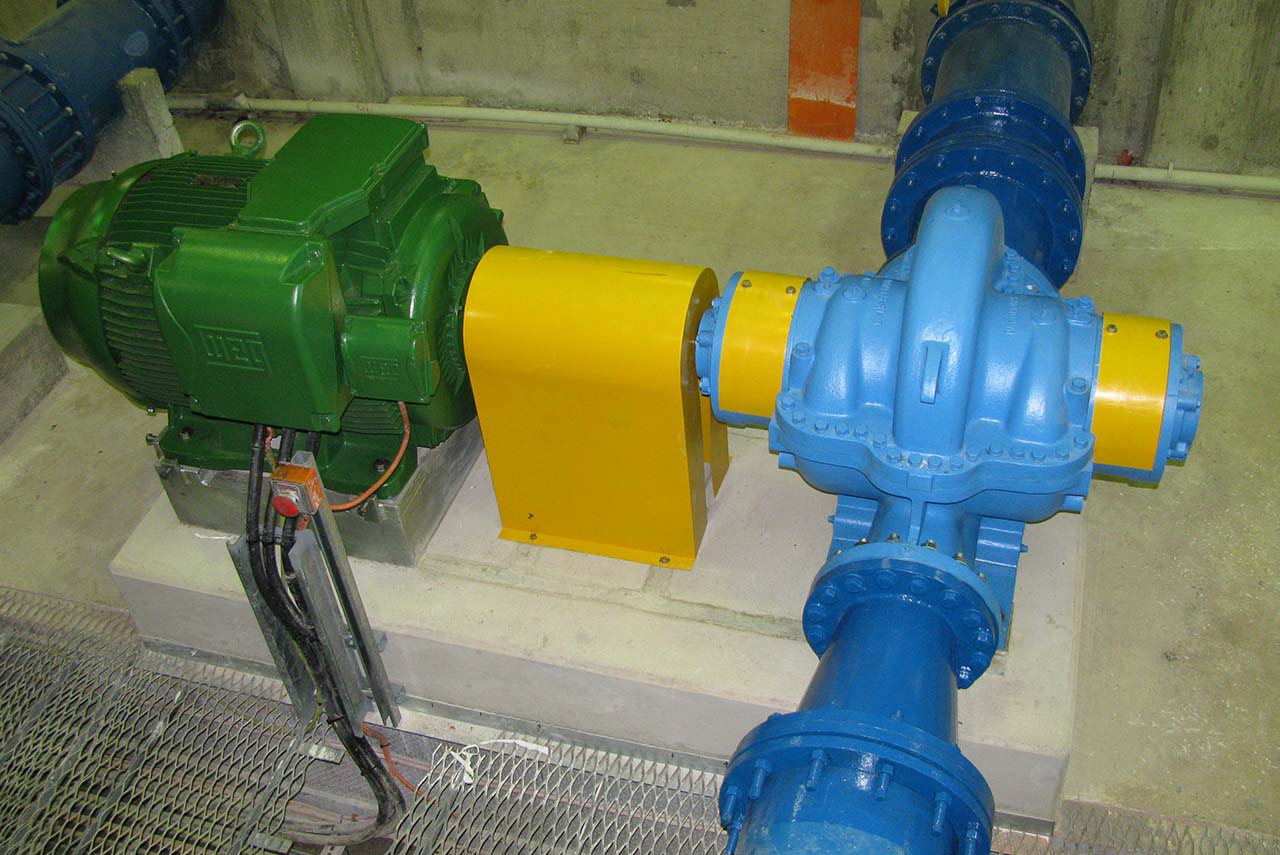
Centrifugal PUMPS
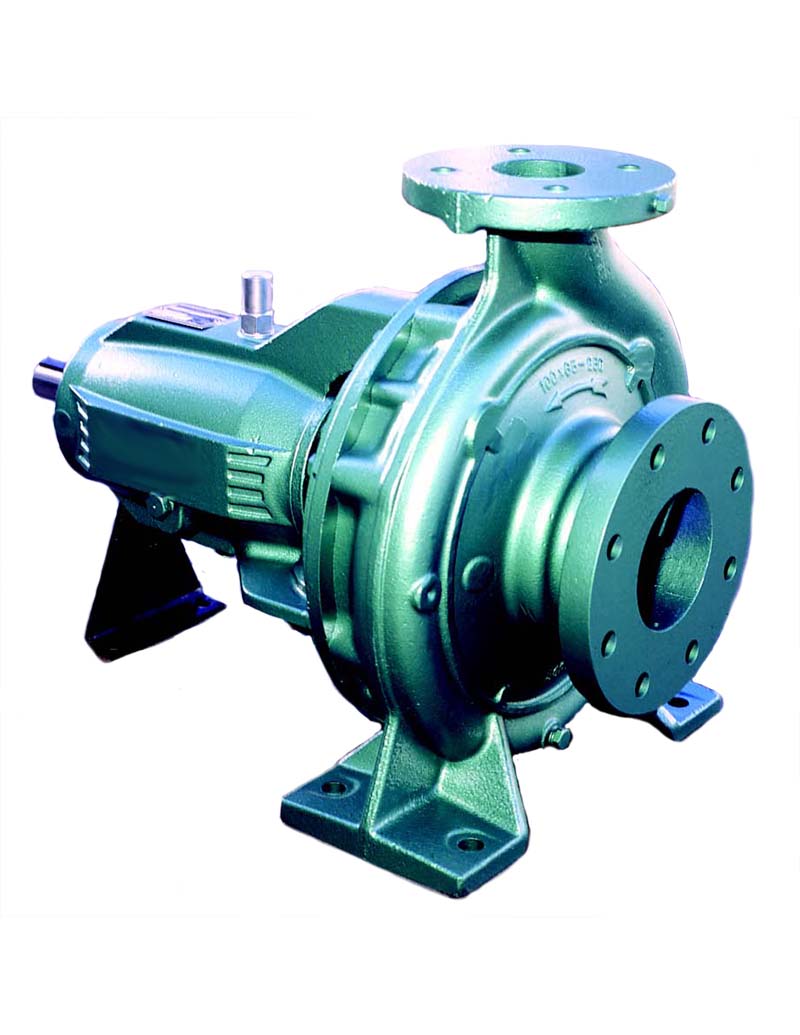
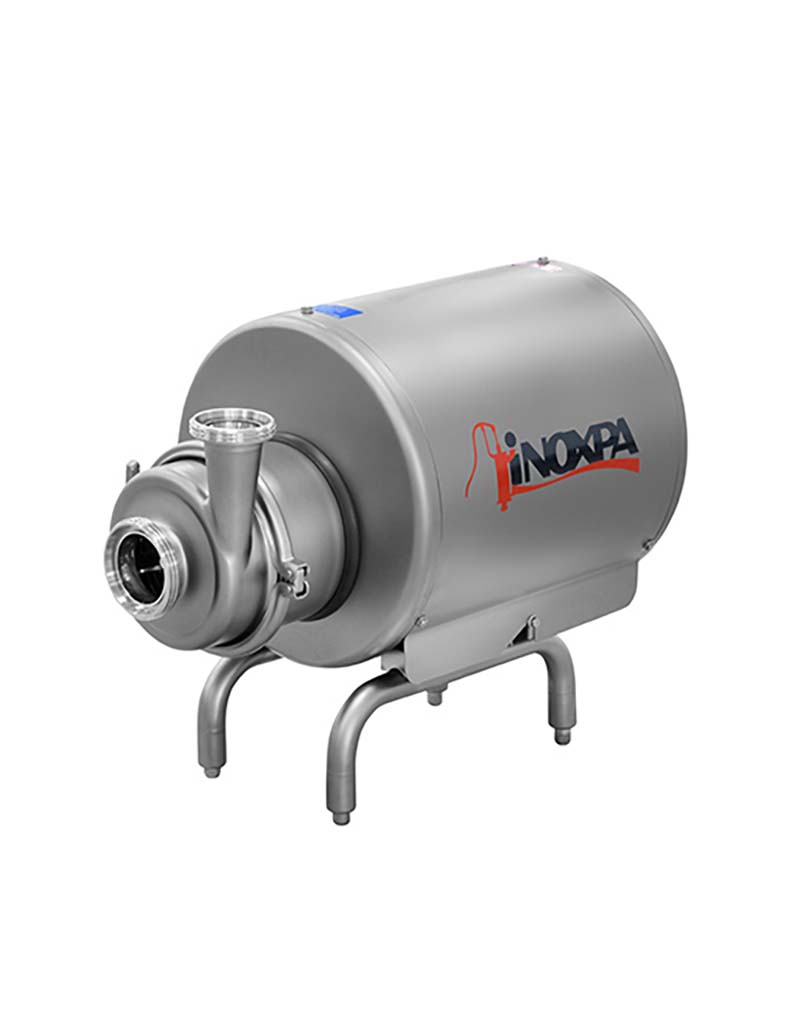
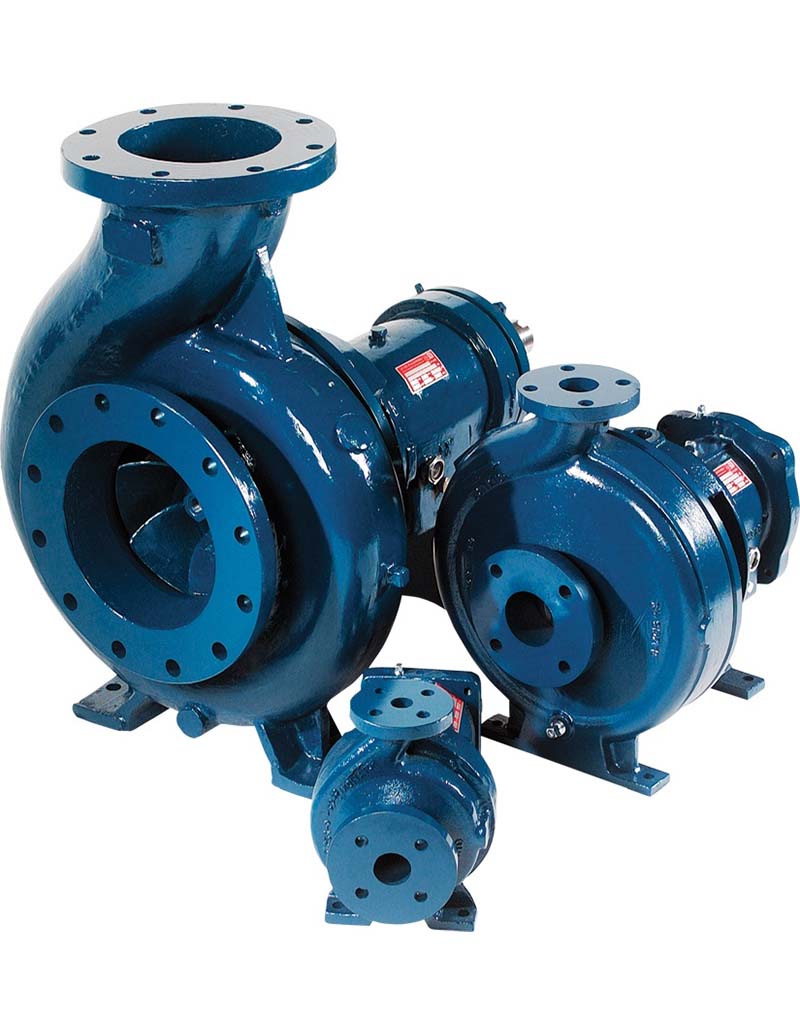
A centrifugal pump is a mechanical device designed to move a fluid by means of the transfer of rotational energy from one or more driven rotors, called impellers. Fluid enters the rapidly rotating impeller along its axis and is cast out by centrifugal force along its circumference through the impeller’s vane tips. The action of the impeller increases the fluid’s velocity and pressure and also directs it towards the pump outlet. The pump casing is specially designed to constrict the fluid from the pump inlet, direct it into the impeller and then slow and control the fluid before discharge.
What are the main features of a centrifugal pump?
There are two main families of pumps: centrifugal and positive displacement pumps. In comparison to the latter, centrifugal pumps are usually specified for higher flows and for pumping lower viscosity liquids, down to 0.1 cP. In some chemical plants, 90% of the pumps in use will be centrifugal pumps. However, there are a number of applications for which positive displacement pumps are preferred.
Your content goes here. Edit or remove this text inline or in the module Content settings. You can also style every aspect of this content in the module Design settings and even apply custom CSS to this text in the module Advanced settings.
Satisfaction Guaranteed
Call us today
1300 336 364